Asset Management
The DRA team can assist businesses through the systematic process of managing cost, risk and performance of the business assets. The DRA process we use has proven to assist in the identifying, recording and action process.
Most businesses in Australia generate revenue by realising value from their assets, whether directly or indirectly.
Asset Management Process
This process is supported by a Standard ISO 55001 to articulate the processes required to achieve the maximum life cycle value of an asset.
Mature businesses generally have systems that have evolved with growth, relying heavily on staff knowledge instead of system competence.
The ISO 55000 suite is gaining acknowledgment as best practice with many major Australian businesses. These businesses are seeking to manage their assets systematically.
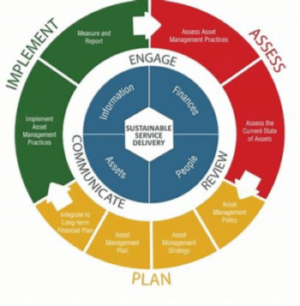

Asset Management Process
This process is supported by a Standard ISO 55001 to articulate the processes required to achieve the maximum life cycle value of an asset.
Mature businesses generally have systems that have evolved with growth, relying heavily on staff knowledge instead of system competence.
The ISO 55000 suite is gaining acknowledgment as best practice with many major Australian businesses. These businesses are seeking to manage their assets systematically.
An assessment completed by one of our competent assessors will identify where opportunities or weaknesses exist in the business. The report will provide clear measurable guidance on where to focus resources and effort.
DRA have ISO 55001 accredited assessors and can partner with organisations for a complete system assessment. We also can conduct individual process assessments in safety, maintenance management and training.
We offer a range of health and safety courses, safety training and WHS consultancy services.
Contact us today for an obligation free quote on any of our services.
Key Personnel

David Randall
CEO – Senior Safety Consultant

Andrew Middleton
Senior Safety Consultant

Clinton Ford
Engineering Consultant
Book a consultation today
Frequently Asked Questions
What is asset management?
What is asset lifecycle?
What are the types of asset management?
– Physical – handling things like fixed asset management, inventory management, infrastructure, and public asset management.
– Financial – managing procurement, developing an investment strategy, controlling budget and costs, handling cash, bonds, and stocks.
– Contractual compliance – streamlines processes like IT asset management, digital asset management, contractual maintenance, and management of intangible assets.
What are the key components of an effective asset management process?
– Preparing an asset register: An inventory list of available assets
– Identify asset conditions and rating system
– Track asset depreciation accurately at timely intervals
– Determine the value of assets and their replacement cost
– Move away from reactive to predictive asset maintenance
– Focus more on change management to ensure database integrity
– Eliminate paperwork and automate tasks like data collection, asset reporting, and more
What are the key components of an effective asset management process?
– Preparing an asset register: An inventory list of available assets
– Identify asset conditions and rating system
– Track asset depreciation accurately at timely intervals
– Determine the value of assets and their replacement cost
– Move away from reactive to predictive asset maintenance
– Focus more on change management to ensure database integrity
– Eliminate paperwork and automate tasks like data collection, asset reporting, and more
What makes up a good asset management process?
– identify the risks and safe operating requirements for the asset from, for example, operations and maintenance manuals
– identify the maintenance requirements to ensure that best practice is being followed, based upon suppliers/manufacturers recommendations
– identify the required legislative, legal and statutory requirements in terms of safe operation and maintenance so as to ensure compliance
– identify the available Codes of Practice, guidance and standards that may inform the organisation of the best practice that may be followed to meet the above requirements
– identify the documentation required for audit and performance measurement purposes.


